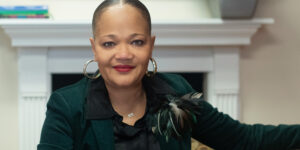Each year there is an average of 20 murders and many more serious injuries in the City of Syracuse as a result of neighborhood violence. Even if residents have had no direct involvement, living in and around violent neighborhoods means they are very likely to know someone who has been shot, stabbed and/or killed. Most are unaware of the effect this is having on them.
A recently developed program is working to address this issue by helping those suffering from violence-related trauma to recover and thrive. In This Together was formed through a partnership between Syracuse University’s Marriage and Family Therapy Center at Falk College and the Syracuse Trauma Response Team. It provides those who work one-on-one with community residents every day with the tools they need to identify signs of trauma and remedy it.
A Community Foundation grant enabled the partner organizations to host group sessions attended by teachers, nurses, physicians, police, therapists, social workers and child specialists who work in high-violence neighborhoods. It also provided transportation vouchers for families to receive grief and trauma services.
“A lot of people don’t know that they’re dealing with trauma and are instead misdiagnosed with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, depression or other illnesses,” said Tamika Otis, project director of Western New York outreach admission for Job Corps, who attended the program. “It’s really important that community counselors are well-versed on how to uncover the root of unresolved trauma. Otherwise everything else is off balance.”
Those indirectly affected by violence frequently struggle with feelings of grief, helplessness and fear, leading to post-traumatic stress, substance abuse, revenge violence and detachment from friends, family and school. This can impede their ability to maintain healthy relationships, gain a proper education or secure a job.
After attending the In This Together introductory workshop, Otis found she had learned helpful techniques that she could use in her job when interacting with local residents who come to her struggling to gain and maintain long-term employment.
“It was one of the best workshops I’ve attended because I learned the different ways trauma can affect us physically, emotionally and mentally,” said Otis. “The trainings taught us how to effectively uncover the trauma that the young people we serve are experiencing and analyze the best way to help solve it.”
“The more community counselors are educated, the easier we can manage and prevent additional trauma,” said Otis. “I believe that with this multi-phase training program in trauma-informed practice we have the information to start to shift environments for our young people.”