The world of dating has been forever-changed by the Internet. Applications such as Tinder, Bumble and Hinge have allowed for individuals separated by time and space to connect based upon shared interests, without ever needing to meet one another face to face. For better or for worse, this has led to an unprecedented level of digital connectivity unlike the world has seen before.
But what if this new technology could be used for a different purpose—for the betterment of communities, outside of pixilated messages and swipes? For Dr. Frank Ridzi, vice president, community investment at the Central New York Community Foundation, the idea wasn’t so farfetched.
Ridzi is a lover of data. He thrives on the excitement of recognizing trends between nonprofit groups in the Central New York community, and using data to allocate aid accordingly. Utilizing the Life Needs Assessment, a survey offered to various non-profits in the area, Ridzi pioneered the concept of “Data Dating.”
The Life Needs Assessment is quite simple; surveyed respondents answer succinct, straightforward questions such as “Do you have dependable and safe transportation when you need it,” and “Do you have long-term housing that you can afford.” Respondents are also asked to provide basic, demographic information on age, race, and neighborhood, among others, to analyze which communities are in need of certain resources.
The most crucial aspect of the survey is that it is completely confidential. Anyone who is served by a nonprofit organization has the opportunity to take the survey. Privacy is integral to data gathering, and the assessment never shares names in the process to protect respondents.
Similar in the way dating apps match users with one another based upon common interests, data dating uses survey responses to pair different nonprofits with one another based upon their clients’ needs and strengths. In all aspects of their operations, where one organization flourishes, another may struggle. Data Dating allows for different organizations to connect based upon mutually beneficial partnerships, and ultimately leads to better services for the communities the nonprofits represent.
PEACE, Inc. used Data Dating resources to partner with organizations that have similar missions to further enhanceo its work. Todd Goehle, community engagement director at PEACE, Inc., cited the importance of holistic data collection and collaboration with other organizations.
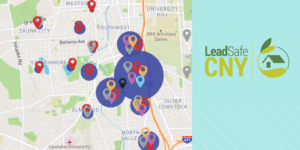
“The data that we’re accumulating doesn’t necessarily reflect the community at large,” he said. “This tool gives us opportunities, especially with live mapping, to identify locations where interventions can be made.”
The survey allows organizations to combine both qualitative and quantitative data to paint a better picture of the needs in communities. For example, during the onset of COVID-19, there was a common narrative that the most need-based resource was food. However, it became clear through surveyed respondents that there was a greater need for things like jobs, assistance paying bills, computers and internet connectivity. This data made it easier for organizations to identify the areas that needed attention and quickly shift resources to address them.
Pairing nonprofits together in order to more efficiently and effectively achieve their goals is the first step in creating a better quality of life for Central New York residents. Not only does the method of Data Dating facilitate a culture of partnership, but it ensures resources are allocated in an equitable and impactful way